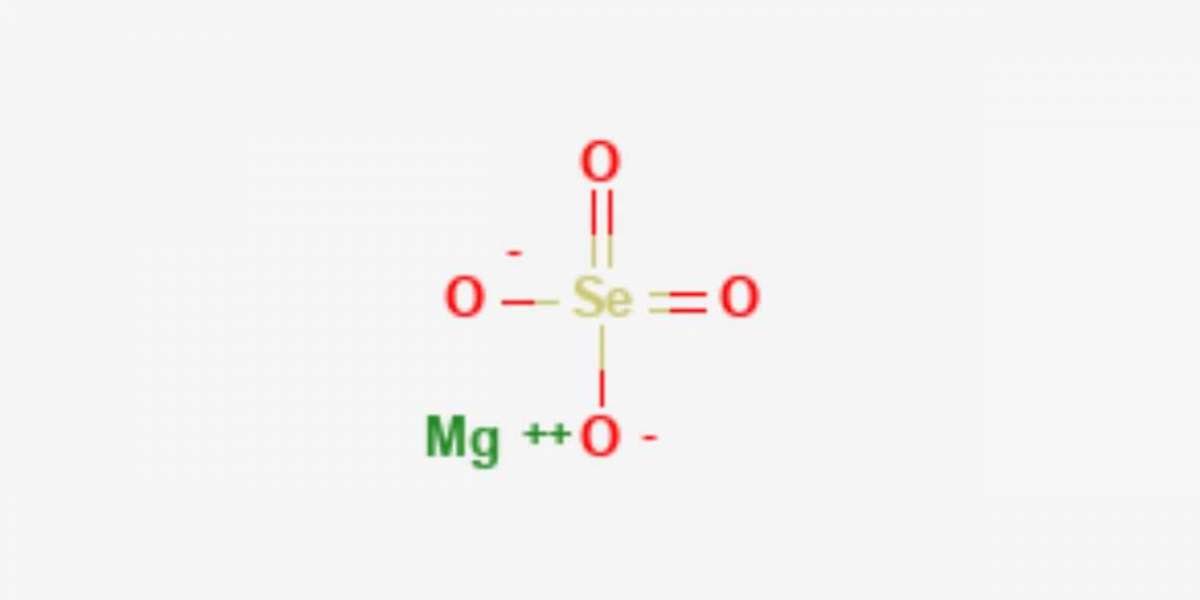
Introduction
Magnesium selenate is a chemical compound consisting of magnesium and selenium, which is used primarily as a nutrient supplement for animals, plants, and in certain industrial applications. It plays an important role in the agricultural sector, particularly in crop production and animal feed, where selenium is an essential micronutrient. The increasing demand for high-quality fertilizers, particularly those enriched with trace elements like selenium, is driving the market for magnesium selenate. In addition, the compound finds applications in the manufacturing of specialty chemicals, electronics, and other industries. Setting up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant involves understanding the chemical production processes, sourcing high-quality raw materials, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the key steps, processes, financial considerations, and market potential of magnesium selenate production.
Industry Overview
The global demand for magnesium selenate is closely linked to the growing agricultural, chemical, and industrial sectors. Selenium is an essential micronutrient that supports various biological functions in animals and plants, and its importance has driven the demand for magnesium selenate as a supplement in fertilizers and animal feed. The agricultural industry, in particular, is a significant consumer of magnesium selenate, where it is used in fertilizers to improve soil quality and boost crop yields. Selenium is a vital trace element that helps enhance the nutritional content of crops and is essential for livestock and poultry growth.
In addition to agriculture, magnesium selenate finds applications in the chemical manufacturing industry as a reagent in specialized chemical processes. As global agricultural production continues to rise to meet food demands, the need for fertilizers enriched with micronutrients like selenium is expected to grow, thus increasing the demand for magnesium selenate.
Market Demand for Magnesium Selenate
The demand for magnesium selenate is primarily driven by several key sectors:
1. Agriculture
- Fertilizers: Magnesium selenate is used in fertilizers as a source of magnesium and selenium, two essential nutrients for plants. Selenium deficiencies in soil can limit crop growth and reduce yield. Magnesium selenate acts as a supplement to provide these vital nutrients.
- Soil Enrichment: It helps improve the quality of soil, providing essential trace elements that contribute to plant health and growth. As the agricultural sector focuses on improving crop yields and soil health, magnesium selenate has gained popularity as a vital ingredient in fertilizers.
- Animal Feed: Selenium is a key component in animal nutrition. Magnesium selenate is added to animal feed to ensure adequate selenium intake, promoting livestock health, improving immune function, and preventing selenium deficiency diseases in animals.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
2. Chemical Manufacturing
- Specialty Chemicals: Magnesium selenate serves as a precursor for the production of other selenium-based compounds used in various chemical applications, such as in the electronics industry, glass production, and in the synthesis of specialty chemicals.
- Reagents in Chemical Reactions: It can also act as a reducing agent or a catalyst in certain chemical reactions, further broadening its industrial application.
3. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
- Electronic Components: Selenium-based compounds, including magnesium selenate, are used in the production of semiconductors, photovoltaic cells, and solar panels. Selenium is an important element in the creation of materials for thin-film solar cells due to its photoelectric properties.
4. Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Sectors
- Nutritional Supplements: Selenium is an essential micronutrient for human health, and magnesium selenate is sometimes used in the production of dietary supplements. It has antioxidant properties and is associated with improving immune function, making it a sought-after ingredient in the nutraceutical industry.
Project Description
Setting up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant involves several stages, including raw material sourcing, production processes, machinery selection, quality control, and packaging. Below is a breakdown of the essential steps involved in the manufacturing process.
Raw Materials
The key raw materials required for magnesium selenate production include:
- Magnesium Compounds: Magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt) or magnesium oxide is typically used as the source of magnesium in the production process.
- Selenium Compounds: Selenium dioxide or sodium selenate is used as the primary source of selenium for the synthesis of magnesium selenate.
- Water: Water is required in the reaction process for dissolving and combining the raw materials.
- Chemicals and Catalysts: Additional chemicals may be needed for controlling the reaction conditions, ensuring optimal yield, and enhancing the quality of the final product.
Manufacturing Process
The production of magnesium selenate involves a chemical reaction between magnesium compounds and selenium compounds. The key steps in the production process are:
1. Preparation of Magnesium and Selenium Solutions
- Magnesium sulfate or magnesium oxide is dissolved in water to create a magnesium solution. Similarly, selenium dioxide or sodium selenate is dissolved in water to create a selenium solution.
2. Reaction and Formation of Magnesium Selenate
The magnesium solution is then combined with the selenium solution in a controlled reaction vessel. The reaction between magnesium and selenium compounds produces magnesium selenate as a precipitate.
The magnesium selenate precipitates out of the solution during the reaction.
3. Filtration and Separation
- The solid magnesium selenate is separated from the remaining solution using filtration or centrifugation. This helps isolate the magnesium selenate from impurities and by-products such as sodium sulfate.
4. Washing
- The precipitate is washed with water to remove any residual soluble impurities and by-products, ensuring the purity of the magnesium selenate.
5. Drying
- The washed magnesium selenate is then dried using rotary dryers or fluidized bed dryers to remove moisture content. Drying is an essential step in ensuring that the magnesium selenate is in powder form for easier handling, packaging, and storage.
6. Grinding
- The dried magnesium selenate is ground into a fine powder using grinding mills or pulverizers. The final particle size is important for its application in agriculture and other industries.
7. Quality Control
- Quality control checks are carried out at various stages of the production process to ensure the product meets industry standards. The final product is tested for purity, particle size, moisture content, and selenium concentration.
8. Packaging
- The final product is packaged in moisture-resistant bags or containers, ensuring that the magnesium selenate is protected during storage and transportation. The packaging is labeled with product information, including the selenium content, weight, and storage instructions.
Machinery and Equipment
Key machinery and equipment required for the production of magnesium selenate include:
- Reaction Vessels: Used to mix and react magnesium and selenium compounds.
- Filtration Equipment: To separate the magnesium selenate precipitate from the solution.
- Dryers: Rotary dryers or fluidized bed dryers to remove moisture from the product.
- Grinding Mills: For grinding the dried magnesium selenate into a fine powder.
- Packaging Machines: Automated equipment for packaging the final product in suitable containers.
Location and Facility
The location of the magnesium selenate manufacturing plant plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of the project. The following factors should be considered when selecting the location:
- Proximity to Raw Materials: The plant should be located near suppliers of magnesium compounds (such as magnesium sulfate) and selenium compounds (such as sodium selenate) to reduce transportation costs.
- Availability of Water: A consistent and reliable water supply is necessary for the chemical reactions and washing stages.
- Infrastructure: The plant should have access to transportation networks (roads, railways, ports) to facilitate the movement of raw materials and finished products.
- Skilled Labor Availability: The plant should be located in an area with access to skilled labor to operate machinery, perform quality control, and maintain production standards.
Market and Sales Strategy
Developing an effective market and sales strategy is key to the success of the magnesium selenate manufacturing plant. The following strategies can help:
- Target Industries: Focus on industries such as agriculture (fertilizer and animal feed), chemicals, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
- Partnerships with Agricultural Companies: Develop partnerships with agricultural companies, feed manufacturers, and fertilizer distributors to ensure a consistent market for the product.
- Branding and Marketing: Promote the product’s high quality, purity, and environmental benefits. Digital marketing, trade shows, and industry events can help raise awareness and build a strong brand presence.
- Distribution Channels: Establish both direct sales channels and a network of distributors to reach a wide range of customers across different industries.
Financial Feasibility
Establishing a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant requires a significant initial investment. The key financial considerations include:
- Capital Investment: Costs for land, construction, equipment, and raw materials are substantial. A detailed capital investment plan should be developed to determine the required funding.
- Operating Costs: These include raw material costs, labor, utilities, maintenance, and logistics.
- Revenue Generation: Revenue will come from the sale of magnesium selenate to industries such as agriculture, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals.
- Break-even Analysis: A break-even analysis should be conducted to understand how long it will take to recover the initial investment and begin generating profits.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental and safety regulations is essential for the success of the plant. Key regulatory considerations include:
- Environmental Regulations: The plant must comply with waste disposal, emissions control, and water usage regulations.
- Health and Safety Standards: Ensuring a safe working environment for employees and complying with occupational health and safety regulations.
- Quality Certifications: The plant should adhere to quality certifications such as ISO 9001 to ensure that the magnesium selenate produced is of high quality and meets industry standards.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au